DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and most alternative organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has an equivalent polymer. Most DNA is found within the cell organ (known as nuclear DNA), however, a small quantity of DNA can even be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). Mitochondria are structures among cells that convert the energy from food into a kind that cells can use.

How does DNA function?
Genes encode proteins that carry out all styles of capabilities for humans (and different residing beings).
The human gene HBA1, for instance, incorporates commands for constructing the protein alpha globin, which is part of hemoglobin, the oxygen-sporting protein in red blood cells, in keeping with the NLM(opens in new tab). To take some other instance, the gene OR6A2 encodes an olfactory receptor, a protein that detects odors withinside the nose, in keeping with the National Center for Biotechnology Information’s Gene database(opens in new tab). Depending on which model of OR6A2 you have, you can love cilantro or assume it tastes like soap, in keeping with an examination posted in 2012 withinside the journal Flavour(opens in new tab).
Although every certainly considered one among your 37.2 trillion cells contains a replica of your DNA, now no longer do all cells construct equal proteins. One motive for that is that molecules known as “transcription elements” latch onto DNA to manipulate which genes get switched on and off, and therefore, which proteins get made when, wherein, and in what portions in every molecular, Live Science formerly reported. DNA additionally receives packaged barely in a different way in exclusive molecular types, and this affects how and wherein transcription elements can snatch onto the molecule.
In addition, epigenetics — which actually means “above” or “on top of” genetics — refers to outside adjustments to DNA that flip unique genes on or off.
For instance, small molecules known as methyl businesses can connect to a DNA strand and save your unique genes from being expressed. Another instance of epigenetics is known as “histone modification,” wherein adjustments to the spool-like protein’s inner chromosomes could make unique segments of DNA greater or much less handy to the proteins that “read” genes. Such epigenetic adjustments to DNA may be exceeded onto destiny generations if the adjustments arise in sperm or egg cells, Live Science formerly reported.
How is DNA packaged inside cells?
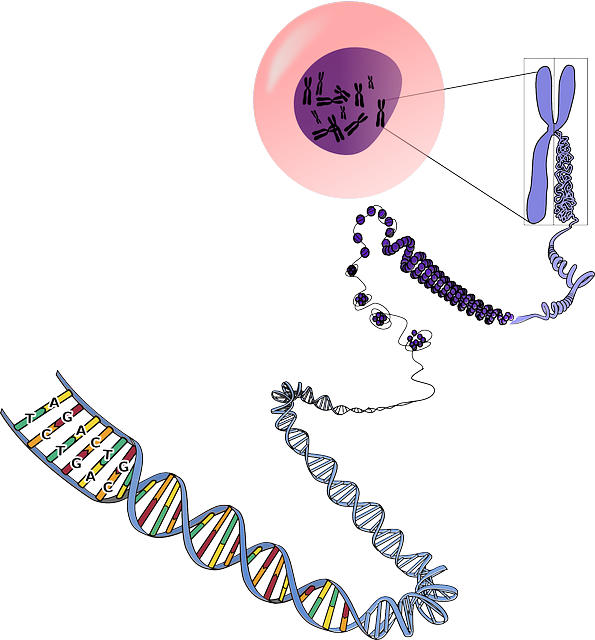
Most cells are distinctly small. For instance, one human by myself includes about one hundred trillion cells. Yet, if all the DNA inside simply this type of cell has been organized right into a single immediate piece, that DNA could be almost metered lengthy! So, how can a great deal of DNA be made healthy inside a cell? The solution to this query lies withinside the method acknowledged as DNA packaging, which is the phenomenon of becoming DNA into dense compact forms.
During DNA packaging, lengthy portions of double-stranded DNA are tightly looped, coiled, and folded in order that they are healthy without problems withinside the cell. Eukaryotes accomplish this feat by wrapping their DNA around unique proteins called histones, thereby compacting it sufficient to healthy withinside the nucleus (. Together, eukaryotic DNA and the histone proteins that maintain it collectively in a coiled shape are called chromatin.
DNA may be similarly compressed thru a twisting method called supercoiling. Most prokaryotes lack histones, however, they do have supercoiled sorts of their DNA held collectively through unique proteins. In each eukaryote and prokaryote, this tremendously compacted DNA is then organized into systems called chromosomes. Chromosomes take extraordinary shapes in extraordinary sorts of organisms.
For instance, maximum prokaryotes have a single round chromosome, while maximum eukaryotes have one or extra linear chromosomes, which frequently seem like X-formed systems. In extraordinary instances for the duration of the lifestyles cycle of a cell, the DNA that makes up the cell’s chromosomes may be tightly compacted right into a shape this is seen below a microscope, or it could be extra loosely disbursed and resemble a pile of string.
For instance, small molecules known as methyl businesses can connect to a DNA strand and save your unique genes from being expressed. Another instance of epigenetics is known as “histone modification,” wherein adjustments to the spool-like protein’s inner chromosomes could make unique segments of DNA greater or much less handy to the proteins that “read” genes. Such epigenetic adjustments to DNA may be exceeded onto destiny generations if the adjustments arise in sperm or egg cells, Live Science formerly reported.
How is data kept in DNA?
The data in DNA is kept as a code created of four chemical bases: A (A), G (G), pyrimidine (C), and T (T). Human DNA consists of regarding three billion bases, and quite ninety-nine % of these bases are equivalent to altogether to people. The order, or sequence, of those bases, determines the knowledge obtainable for building and maintaining an organism, almost like the approach during which letters of the alphabet seem in an exceedingly bound order to make words and sentences.
DNA bases combine up with every other, A with T and C with G, to form units known as base pairs. every base is additionally connected to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a command, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are organized in 2 long strands that kind of a spiral is known as a helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat sort of a ladder, with the bottom pairs forming the ladder’s rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder.
A vital property of deoxyribonucleic acid is that it will replicate, or build copies of itself. every strand of DNA within the double helix can function as a pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases. this is often vital once cells divide because each new cell must have a precise copy of the DNA gift in the recent cell.DNA is a helix-shaped by base pairs connected to a sugar-phosphate backbone
How is DNA sequenced?

Genes encode proteins that carry out all styles of capabilities for humans (and different residing beings). The human gene HBA1, for instance, incorporates commands for constructing the protein alpha globin, which is part of hemoglobin, the oxygen-sporting protein in red blood cells, in keeping with the NLM(opens in new tab).
To take some other instance, the gene OR6A2 encodes an olfactory receptor, a protein that detects odors withinside the nose, in keeping with the National Center for Biotechnology Information’s Gene database(opens in new tab). Depending on which model of OR6A2 you have, you can love cilantro or assume it tastes like soap, in keeping with an examination posted in 2012 withinside the journal Flavour(opens in new tab).
Although every certainly considered one among your 37.2 trillion cells contains a replica of your DNA, now no longer do all cells construct equal proteins. One motive for that is that molecules known as “transcription elements” latch onto DNA to manipulate which genes get switched on and off, and therefore, which proteins get made when, wherein, and in what portions in every molecular, Live Science formerly reported.
DNA additionally receives packaged barely in a different way in exclusive molecular types, and this affects how and wherein transcription elements can snatch onto the molecule. In addition, epigenetics — which actually means “above” or “on top of” genetics — refers to outside adjustments to DNA that flip unique genes on or off.
For instance, small molecules known as methyl businesses can connect to a DNA strand and save your unique genes from being expressed. Another instance of epigenetics is known as “histone modification,” wherein adjustments to the spool-like protein’s inner chromosomes could make unique segments of DNA greater or much less handy to the proteins that “read” genes. Such epigenetic adjustments to DNA may be exceeded onto destiny generations if the adjustments arise in sperm or egg cells, Live Science formerly reported.
Who discovered DNA?

The discovery of DNA’s double-helix shape is credited to the researchers James Watson and Francis Crick, who obtained a Nobel Prize in 1962 for their work with fellow researcher Maurice Wilkins. Many consider that Rosalind Franklin needs to take delivery of credit additionally, given that she made the progressive picture graph of DNA’s double-helix shape, which became used as proof without her permission.
